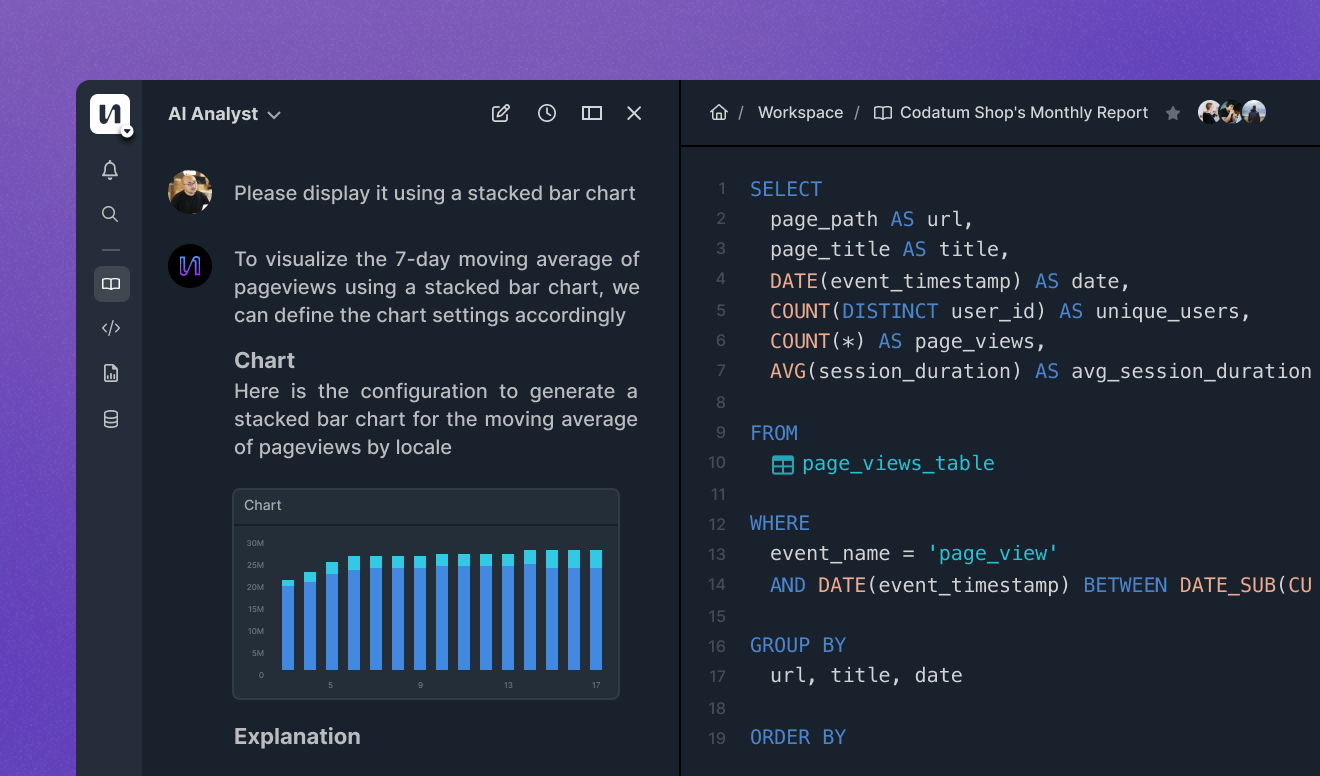
In the data analysis tool industry, there has long been a dilemma between “simplicity” and “advanced analysis.”
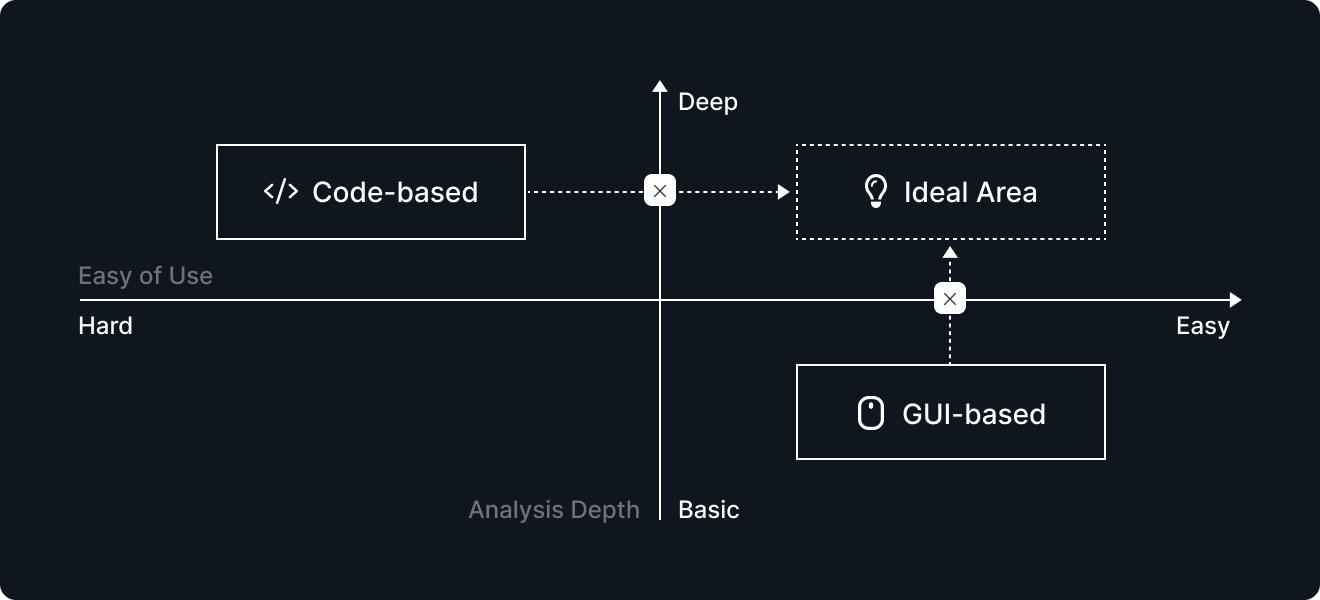
GUI-based BI tools prioritize “making it easy for anyone to use.” By allowing users to create tables and charts with drag-and-drop functionality, these tools have made data utilization accessible. However, such tools often limit users’ ability to perform advanced, customized analysis.
In contrast, code-based environments like Data Workspace ([Note 1]) empower users to perform “advanced analysis in a flexible way” using SQL and Python. But these require specialized skills, which can be a barrier for many users.
Recent advancements in AI, however, suggest that this situation could change dramatically.
The latest AI can generate code in natural language, understand its purpose, and explain it. Through interaction with users, AI can interpret intent and provide relevant support. This opens the door to balancing “ease of use” with “advanced analysis.”
Yet, a key question remains: how should we incorporate AI? Should we aim for complete automation, or should we strive to support human understanding and growth?
One answer lies in combining “Data Workspace with AI.” This article will explore the current possibilities of this approach.
Code x AI Approach: A Common Language Between Humans and Systems
When exploring ways to leverage AI, a code-based approach is particularly promising.
Today’s AI models are trained on vast amounts of real-world code from platforms like GitHub, learning patterns that “actually work.” This allows AI to generate understandable, executable code—one of its core strengths.
However, the value of the code-based approach doesn’t stop at execution.
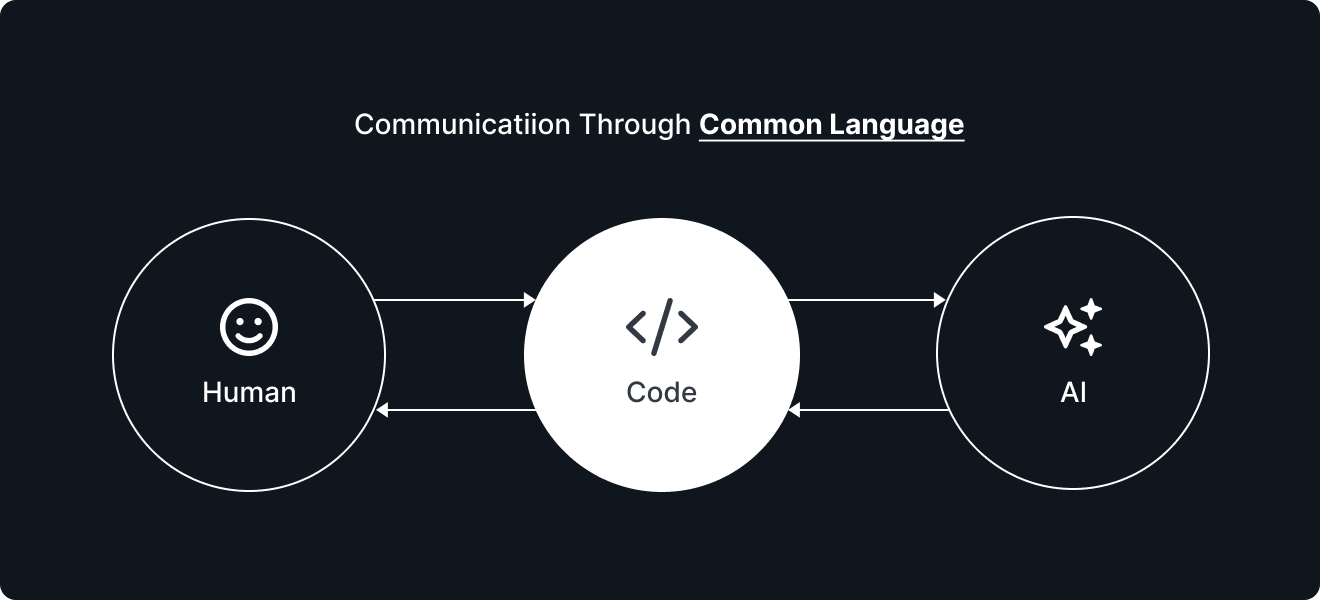
AI-generated code goes beyond mere text; it’s “executable,” meaning it can interact with data and systems. For example, it can generate code that extracts, processes, and visualizes data, executing commands in real time.
Even more importantly, code serves as a “common language” between humans and AI, enabling collaboration. Generated code is not a black box; humans can read, understand, and modify it as needed, guiding AI to improve its suggestions. This mutual understanding makes effective collaboration between AI and humans possible.
The success of GitHub Copilot demonstrates the potential of this approach. Copilot doesn’t just suggest code; it provides specific examples that help developers understand and refine their work.
By combining these elements, a code-based platform integrated with AI becomes more than just a tool. It becomes a “partner” in fostering human growth and development.
Two Approaches to Data Analysis x AI
When looking at data analysis through this lens, we see two main approaches.
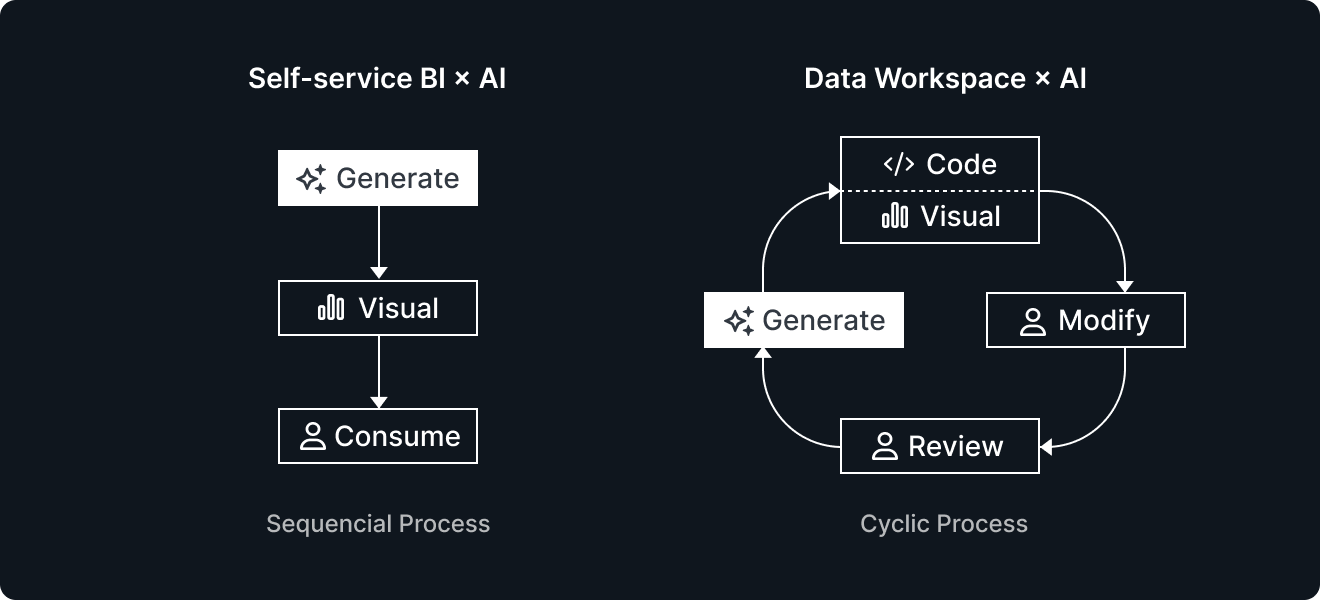
Self-service BI x AI
This approach embeds AI into traditional self-service BI tools, allowing users to make requests like “Show the sales trend” or “Display last month’s profits by department in a pie chart.” AI then generates suitable charts automatically, making the process intuitive and accessible.
However, challenges remain with this approach:
Black Box Processing: Users can’t see the data processing flow, making it hard to assess accuracy.
Limited Customizability: Handling complex analysis requests or extending beyond existing functions is difficult.
Data Workspace x AI
The other approach is embedding AI into Data Workspace, where AI works alongside code to support analytical work. Key features include:
Transparency: Users can verify generated code, follow data processing steps, and handle edge cases.
Customizability: Modifying code, adding unique processes, and expanding for advanced analysis are all possible.
With this approach, AI doesn’t merely “consume” code; it acts as a “common language” that encourages collaboration.
Building a Data-Driven Organization Through Data Workspace x AI
This new relationship between humans and AI through Data Workspace x AI brings fresh insights for building data-driven organizations.
Coexistence of Simplicity and Advanced Analysis
Data Workspace allows complex aggregations and advanced analysis to be expressed entirely through code. Even non-technical users can leverage high-level code through natural dialogue with AI, breaking the trade-off between “simplicity” and “advanced analysis.”
Learning
For users with technical skills, AI-generated code can be a valuable learning tool, helping them discover new techniques or recall forgotten methods. Less technical users can benefit by deepening their understanding through completed code examples.
A Collaborative Cycle
In a transparent Data Workspace environment, humans and AI can generate analysis content collaboratively. AI-generated code is validated, improved, and refined in response to user feedback. This creates a cycle that pushes analytical content forward.
The combination of Data Workspace and AI enables a new partnership, utilizing the strengths of both humans and AI.
Case Studies: The Latest Developments in Data Workspace x AI
Many products are moving forward with AI integration. Each offers a unique approach to reshape data analysis. Here are a few examples:
Deepnote x AI: Intelligent completion and explanation by understanding the entire notebook context.
Hex x AI: Supports everything from SQL and Python generation to data interpretation.
Querybook x AI: An AI assistant for optimized query generation and SQL guidance.
PopSQL x AI: Team-wide query creation with AI assistance, promoting knowledge sharing.
Codatum x AI: Our own product, Codatum, also has a powerful AI Assistant as a data analysis partner. By connecting with Catalog and Notebooks, Codatum supports seamless analysis, handling both simple and complex queries.
This functionality continues to evolve, and we’ll keep you updated on new developments.
In Conclusion
This article explored the new partnership between humans and AI through Data Workspace x AI, which has the potential to shape a new data-driven organization structure. Although few products have fully realized this state, advances in AI and product evolution suggest that the future is closer than we think.
As Codatum evolves in line with this article, we aim to create a form of data analysis that bridges humans and AI. Visit Codatum’s website to experience its possibilities.
[Note 1] There are multiple definitions for Data Workspace. Among them:
An environment where data preparation, modeling, and analysis are centrally managed.
An environment where “technical users” can perform and share complex data operations.
These two definitions are often used. Since the latter interpretation is more common in the context of Modern Data Infrastructure (Stack) literature, this article uses “Data Workspace” with that meaning.
References: